What is Maven?
Maven is a powerful project management tool that is based on POM (project object model). It is used for project build, dependency, and documentation. It simplifies the build process like ANT. But it is too much advanced than ANT.
In short terms, we can tell maven is a tool that can build and manage any Java-based project. Maven makes the day-to-day work of Java developers easier and generally helps with the comprehension of any Java-based project.
Maven Architecture
This diagram, provided by Apache itself, gives the best scope of Maven’s architecture.
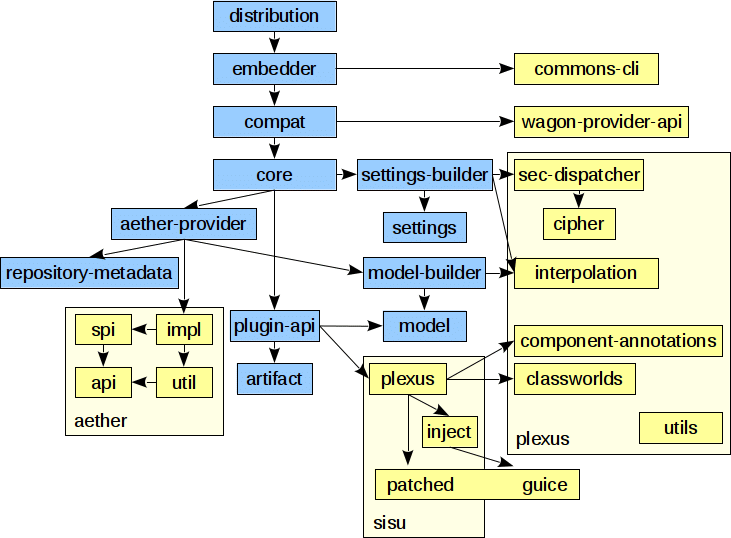
Mavenis written in Java and is used to build projects written in C#, Scala, Ruby, etc. Based on the Project Object Model (POM), this tool has made the lives of Java Developers easier while developing reports, checking to build, and testing automation setups.
What Maven Does?
Maven does a lot of helpful tasks like
- We can easily build a project using maven.
- We can add jars and other dependencies of the project easily using the help of maven.
- Maven provides project information (log document, dependency list, unit test reports etc.)
- Maven is very helpful for a project while updating the central repository of JARs and other dependencies.
- With the help of Maven, we can build any number of projects into output types like the JAR, WAR etc without doing any scripting.
- Using maven we can easily integrate our project with a source control system (such as Subversion or Git).
Core Concepts of Maven
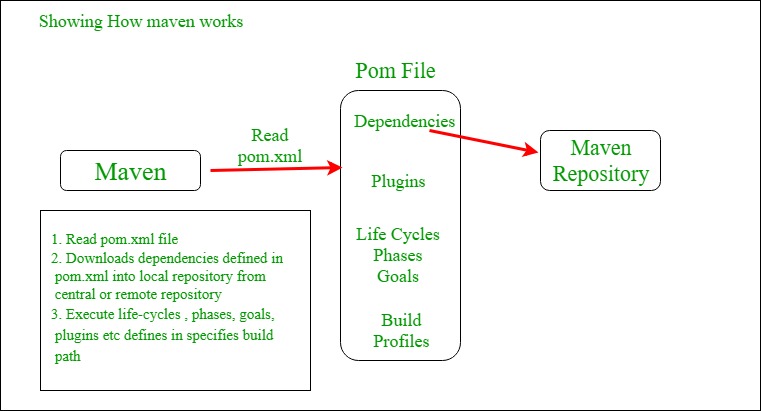
POM Files: Project Object Model(POM) Files are XML file that contains information related to the project and configuration information such as dependencies, source directory, plugin, goals, etc. used by Maven to build the project. When you should execute a maven command you give maven a POM file to execute the commands. Maven reads the pom.xml file to accomplish its configuration and operations.
Dependencies and Repositories: Dependencies are external Java libraries required for Project and repositories are directories of packaged JAR files. The local repository is just a directory on your machine hard drive. If the dependencies are not found in the local Maven repository, Maven downloads them from a central Maven repository and puts them in your local repository.
Build Life Cycles, Phases and Goals: A build life cycle consists of a sequence of build phases, and each build phase consists of a sequence of goals. Maven command is the name of a build lifecycle, phase or goal. If a lifecycle is requested executed by giving maven command, all build phases in that life cycle are executed also. If a build phase is requested executed, all build phases before it in the defined sequence are executed too.
Build Profiles:Build profiles a set of configuration values that allows you to build your project using different configurations. For example, you may need to build your project for your local computer, for development and test. To enable different builds you can add different build profiles to your POM files using its profiles elements and are triggered in a variety of ways.
Build Plugins: Build plugins are used to perform a specific goal. you can add a plugin to the POM file. Maven has some standard plugins you can use, and you can also implement your own in Java.
Maven Repository
Maven repositories are directories of packaged JAR files with some metadata. The metadata are POM files related to the projects each packaged JAR file belongs to, including what external dependencies each packaged JAR has. This metadata enables Maven to download dependencies of your dependencies recursively until all dependencies are downloaded and put into your local machine.
Maven has three types of repositories:
- Local repository
- Central repository
- Remote repository
Maven searches for dependencies in this repositories. First maven searches in Local repository then Central repository then Remote repository if Remote repository specified in the POM.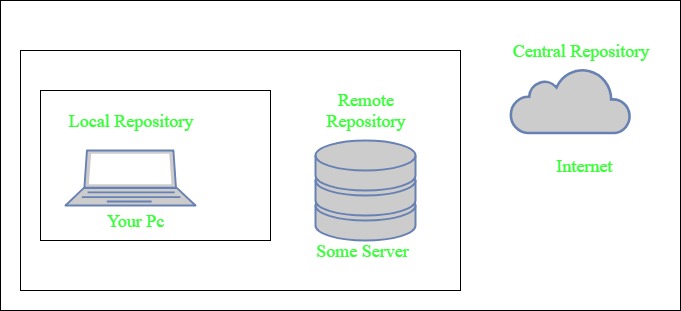
- Local repository- A local repository is a directory on the machine of the developer. This repository contains all the dependencies Maven downloads. Maven only needs to download the dependencies once, even if multiple projects depend on them (e.g. ODBC).
By default, the maven local repository is the user_home/m2 directory. - Central repository- The central Maven repository is created Maven community. Maven looks in this central repository for any dependencies needed but not found in your local repository. Maven then downloads these dependencies into your local repository. You can view the central repository by this link.
- Remote repository- remote repository is a repository on a web server from which Maven can download dependencies.it often used for hosting projects internal to the organization. Maven then downloads these dependencies into your local repository.
How to Use Maven?
When you’re ready to start using Maven, keep these three things in mind:
- Configure Maven in Java, using Project Object Model (POM) found in a pom.xml file.
- All Maven-related configuration settings are found in the POM. You can edit and configure plug-ins in the <plugins> tag of a pom.xml file.
- Maven provides default settings for configurations, so you don’t have to add every configuration into the pom.xml file.
Pros and Cons of using Maven
Pros:
- Maven can add all the dependencies required for the project automatically by reading the pom file.
- One can easily build their project to the jar, war, etc. as per their requirements using Maven.
- Maven makes it easy to start projects in different environments and one doesn’t need to handle the dependencies injection, builds, processing, etc.
- Adding a new dependency is very easy. One has to just write the dependency code in the pom file.
Cons:
- Maven needs the maven installation in the system for working and the maven plugin for the ide.
- If the maven code for an existing dependency is not available, then one cannot add that dependency using maven.
Reference: https://maven.apache.org/guides/getting-started/index.html
 Cloud AMOG Be a Part of the Largest Cloud Community
Cloud AMOG Be a Part of the Largest Cloud Community